Circle
Circle is a locus of a moving point on
the plane surface, which moves in such a way that its distance from a fixed
point is always the same.
In the
adjoining figure, P is moving point with the same distance from a fixed point
O. The closed figure PABC is a circle.
********************
10 Math Problems officially announces the release of Quick Math Solver and 10 Math Problems, Apps on Google Play Store for students around the world.
********************
********************
Definitions of basic terms of circle
CentreThe fixed point in the circle from where each and every point of its circumference are equidistant is called the centre of the circle. In the figure adjoining, O is the centre of circle. |
CircumferenceThe curved boundary or rim of a circle which is equidistant from its centre is called circumference of the circle. The circumference of circle is also known as the perimeter of the circle. In the given figure curve line ABCD is the circumference of the circle. It is generally denoted by ‘c’. |
RadiusA line segment which joins the centre of the circle and any point on the circumference of the circle is called radius of the circle. The plural form of radius is radii. The radii of a circle are equal and is denoted by ‘r’. In the given figure OP = OQ = OR = OS = r. |
DiameterThe line segment passing through the centre and joining the two points of circumference of a circle is called its diameter. In the given circle, AC is a diameter. It is generally denoted by ‘d’. The length of the diameter is twice the radius of circle. ∴ d = 2r, where r is the radius of circle. |
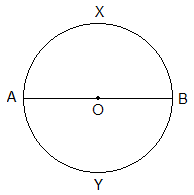
Semi-circleA diameter of a circle divides a circle into two equal halves and each half is called the semi-circle. In the given figure, AXB and AYB are semi-circles. |
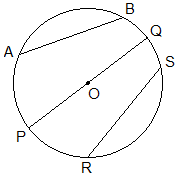
ChordA line segment which is formed by joining any two points on the circumference of a circle is called a chord of the circle. In the figure, PQ, AB and RS are the examples of the chords. A diameter is the longest chord of any circle. |
ArcA portion of the circumference of a circle is called an arc. In the given circle, ABC and CDA are the minor and major arcs respectively. |
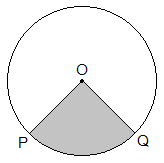
SectorThe region enclosed by any two radii and the arc of a circle is called a sector of the circle. In the figure, the shaded region POQ is an example of a sector. There are minor sector and major sector. The shaded region is a minor sector and unshaded region is a major sector. |
SegmentA part of the circle which is enclosed by an arc and a chord is called the segment of a circle. The part of the circle which is less than semi- circle is called minor segment. In the figure, the shaded part is the minor segment. The part of the circle which is greater than a semi-circle is called the major segment. In the figure, the unshaded part is the major segment. The major and minor segments are known as the alternate segments of each other of the circle. |
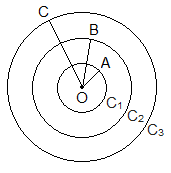
Concentric CirclesTwo or more circles on the same plane having the same centre but different radii are called concentric circles. In the figure, C1, C2 and C3 are three circles having the same centre O but different radii OA, OB and OC respectively. So, these three circles are concentric circles. |
Intersecting CirclesIf two circles with different centres intersect each other at two points, then the circles are called intersecting circles. In the figure two circles with centres P and Q intersect each other at two points A and B. These two circles are known as the intersecting circles. The points are called intersecting points. A chord AB is formed by joining the points A and B. It lies in both circles. So it is called the common chord. A line formed joining the centres P and Q. The line PQ is called the line of centre. The line of centre is perpendicular bisector of the common chord. |
Pie (π)
The ratio of circumference to diameter of
any circle is always the constant, whose value is 22/7 or 3.14. It is denoted
by the Greek letter π(pie).
i.e.
π = Circumference/diameter = c/d = 22/7 = 3.14
Perimeter of Circle
Total length of curved boundary of a
circle is called the perimeter or circumference of the circle. It is given by
the formula,
Circumference
(c) = 2πr or πd
Area of circle
Total surface on the plane covered by the
circumference of a circle is called the area of circle. It is given by the
formula,
Area
of circle (A) = πr2 or πd2/4
You can comment your
questions or problems regarding the Circle
here.












0 comments: