
Triangle | What is Triangle?
 A closed plane figure formed by three line segments is
called a triangle. It is denoted by the symbol Δ.
A closed plane figure formed by three line segments is
called a triangle. It is denoted by the symbol Δ.
In the figure alongside, PQR is a closed plane figure formed
by three line segments PQ, QR and RP. So it is a triangle. It is represented by
ΔPQR. The points P, Q and R are called the vertices of the triangle PQR.
Types of triangles on the basis of sides
On the basis of sides there are three types of triangles:
 i. Scalene
Triangle:
i. Scalene
Triangle:
A triangle having non of the sides equal is called a scalene triangle. In
the given triangle, MN ≠ NP ≠ PM. So ΔMNP is a scalene triangle.
ii. Isosceles
Triangle:
A triangle with having two sides equal is called an isosceles triangle. In the
given triangle, PQ = PR = 5 cm. So, ΔPQR is an isosceles triangle.
Note:
Base angles are always equal of an isosceles triangle. In the given figure ∠PQR = ∠PRQ.
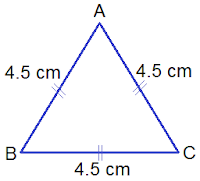 iii. Equilateral Triangle:
iii. Equilateral Triangle:
A
triangle with having all three sides equal is called an equilateral triangle. In the given
triangle, AB = BC = AC = 4.5 cm. So, ΔABC is an equilateral triangle.
Note:
All
angles of an equilateral triangle are 60°. An equilateral triangle holds all
the properties of an isosceles triangle.
Types of triangles on the basis of angles
On
the basis of angles, there are three types of triangles:
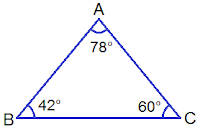 i. Acute Angled Triangle:
i. Acute Angled Triangle:
If all
the angles of a triangle are less than 90° or acute angles, then it is called
an acute angled triangle. In the given triangle, each angle of the triangle is
less than 90°. So, ΔABC is an acute angled triangle.
 ii. Obtuse Angled Triangle:
ii. Obtuse Angled Triangle:
The
triangle with one angle is obtuse angle or more than 90° is called an obtuse
angled triangle. In the given figure, ∠RMN is an obtuse
angle. So, ΔMNR is an obtuse angled triangle.
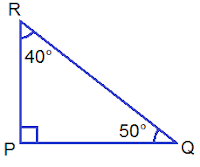 iii. Right Angled Triangle:
iii. Right Angled Triangle:
The
triangle with one angle a right angle or equal to 90° is called a right angled
triangle.
In the
given figure, ∠PQR is 90°. So, ΔPQR
is a right angled triangle.
Note:
If a right angled
triangle has two sides equal, then it is called a right angled isosceles
triangle.
Properties of triangle:
1. Sum of three angles of a triangle is always 180°.
2. Base angles of an isosceles triangle are always equal.
3. All angles of an equilateral triangle are equal to 60° each.
4. Base angles of a right angled isosceles triangle are equal to
45° each.
5. If any two angles of a triangle are equal, then the sides opposite to
them are also equal.
6. The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of two
opposite interior angles.
7. The sum of two sides of a triangle is greater than the third
side.
8. In any triangle, the side opposite to greater angle is longer
than the side opposite to the smaller angle.
9. The line drawn from the vertex of an isosceles triangle to the
mid point of its base is perpendicular to the base.
10.The bisector of the vertical angle of an isosceles triangle is always perpendicular
to the base.
11. The line joining mid-points of any two sides of a triangle is parallel to third side and is half the length of third side.
********************
10 Math Problems officially announces the release of Quick Math Solver and 10 Math Problems, Apps on Google Play Store for students around the world.
********************
********************
You can comment your questions or problems regarding the triangle here.



0 comments: