
Unitary method is a
popular method in mathematical calculation. This method helps us to find the value
of unit quantity from the gross value, and from the value of that unit quantity, we
can find the value of the required quantity.
********************
10 Math Problems officially announces the release of Quick Math Solver and 10 Math Problems, Apps on Google Play Store for students around the world.
********************
********************
For the calculation of unit value, we have to either divide or multiply for the direct or indirect variation quantities. And then, we find the required number of quantities by multiplying or dividing accordingly.
Before we proceed to the unitary method,
let us have an idea about direct variation and indirect variation.
Direct variation
If two quantities are so related that the increase or decrease in one causes the corresponding increase or decrease in the other, they are said to be in direct variation. Let us take an example of no. of copies and their cost:

Above table shows that if the number of
copies increases the total cost also increases. So the number of copies and
their cost are in direct variation. To find the unit value for such quantities
we have to divide the gross value by the number of quantities. And then, we
have to multiply the unit value with the required number of quantities to find
the required value. For example:
“If the cost of 5 copies is Rs. 250, find the cost of 8 copies.”
Solution: Here,
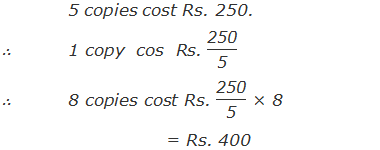
∴ The cost of 8 copies is Rs. 400.
Indirect variation
If two quantities are so related that the
decrease or increase in one causes the corresponding increase or decrease in
the other is called indirect variation.
Let us take an example of the number of men and their working days:
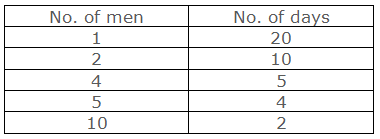
Above table shows that if the number of
men increases the working days decreases. So the number of men and working days
are in indirect variation. To find the unit value for such quantities we have
to multiply the gross value by the number of quantities. And then, we have to
divide the unit value by the required number of quantities to find the required
value. For example:
“If 4 men can do a work in 5 days, in how many days 10 men can do the
same work?”
Solution: Here,

∴ 10 men can do the same work in 2 days.
Worked Out Examples
Example 1:
If 10 kg of mangoes cost Rs. 500 then what will be the cost for 15 kg?
Solution: Here,

∴ 15 kg
mangoes cost Rs. 750.
Example 2:
The price of 20 books is Rs. 3000. How many books can be bought for Rs. 1950?
Solution: Here,

∴ 13 books can be bought for Rs. 1950.
Example 3:
If ¾ of a man’s income is Rs. 3000, what will be ¼ of his income?
Solution: Here,

∴ ¼ of his income is Rs. 1000.
Example 4:
If a work can be completed by 20 people in 45 days. How long will it take to
complete the same work by 15 people?
Solution: Here,

∴ It will take 60 days to complete the same work by 15 people.
Example 5:
A garrison of 800 men has provision for 120 days. How many men should be added
to finish the provision in 100 days?
Solution: Here,

∴ 960 – 800 = 160 men should be added to finish the provision
in 100 days.
Do you have any questions regarding the unitary method?
You can ask your
questions or problems here in the comment section below.



Very easy
ReplyDeletetwo pipes P and Q can fill a tank in 24 minutes and 30 minutes respectively. both pipes are opened together and the first pipe is closed after 8 minutes. after how many minutes the tank will be filled?
ReplyDelete