
Height and Distance
Trigonometric ratios are used to solve the problems related to height and distance. This is one
of the important applications of
trigonometry. It helps to find the height of the objects like tree,
building, tower, etc., and the distance between the objects.
********************
10 Math Problems officially announces the release of Quick Math Solver and 10 Math Problems, Apps on Google Play Store for students around the world.
********************
********************
While finding such height and distances, we have to solve the right angled triangle. For example, in the given figure, AB is the height of a tree, BC is the distance between the tree and the observer at C.
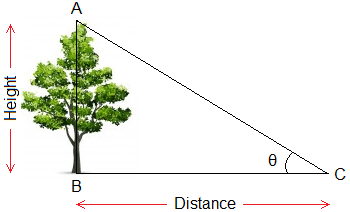
Here, if θ and BC are known, we can calculate the height of tree
AB, or if θ and AB are known, we can calculate the distance between the tree
and the observer by using trigonometric ratio.
Angle of elevation and depression
In the figure given below, an observer is looking at the top of a tower. Here, OA is called the line of sight and OB is the horizontal line.

∠BOA is the angle between the upward line of sight and the horizontal line. Here, ∠BOA is called the angle of elevation.
Thus, the angle made by an upward line of sight with the horizontal line is known as the angle of elevation.
And, in the figure given below, ∠BOA is the angle between the downward line of sight and the horizontal line. Here, ∠BOA is called the angle of depression.

Thus, the angle made by a downward line of sight with the horizontal
line is known as angle of depression.
In the figure given below, the horizontal lines AC and BO are parallel to each other. The angle of depression CAO and the angle of elevation BAO are alternate angles between parallel lines.

∴ ∠CAO = ∠BAO, i.e. Angle of
depression = Angle of elevation.
The instrument which is used to measure the angle of elevation
or the angle of depression is called Theodolite.
Worked Out Examples
Example 1: A man observes the top of a tower 40 m high and finds the elevation
of 30°. Find the distance between the man and the foot of the tower.
Solution:
Let AB be the height of the tower and BC be the distance between the foot of the tower and the man.

Here,
AB = 40 m
Angle of elevation, ∠BCA = 30°
In right angled triangle ABC,
tan30° = p/b = AB/BC = 40/BC
or, 1/√3 = 40/BC
or, BC = 40√3 = 40 ×
1.732 = 69.28 m
So, the required distance is 69.28 m.
Example 2: An electric pole 20 m high is supported by a wire fixing its one
end on the ground at some distance from the pole. If the wire joining the top
of the pole is inclined to the ground at an angle of 30°, find the length of
the wire.
Solution:
Let AB be the height of the pole and AC be the length of the wire.

Here,
AB = 20m.
Angle of elevation, ∠BCA = 30°
In right angled triangle ABC,
sin30° = p/b = AB/AC = 20/AC
or, ½ = 20/AC
or, AC = 40.
So, the required length of the wire is 40m.
Example 3: The circumference of a circular pond is 176m and a pillar is fixed
at the centre of the pond. If a person finds the angle of elevation of 60° of
the top of the pillar from any point on the bank of the pond, find the height
of the pillar above the water pillar.
Solution:
Let AB be the height of the pillar above the water level and BC be the radius of the pond.

Here,
Circumference of pond = 176m
i.e. 2πr = 176
or, 2 × 22/7 × BC = 176
or, 44/7 × BC = 176
or, BC = 176 × 7/44
or, BC = 28m
The angle of elevation, ∠BCA = 60°
Now, in right angled triangle ABC,
tan60° = p/b =
AB/BC = AB/28
or, √3 = AB/28
or, AB = 28√3 = 28 ×
1.372 = 48.5
So, the required height of the pillar is 48.5m.
Example 4: A man 1.5m tall standing at a distance of 50m from a tree observes
the angle of elevation of the top of the tree is 45°. Find the height of the
tree.
Solution:
Let CE be the height of the tree, AB be the height of the man and BC is the distance between the foot of the tree and the man.

Here,
AB = 1.5m
BC = 50m
Angle of elevation, ∠DAE = 45°
In rectangle ABCD,
DC = AB = 1.5m
AD = BC = 50m
In right angled triangle ADE,
tan45° = p/b =
ED/AD = ED/50
or, 1 = ED/50
or, ED = 50m
Now, CE = ED + DC
= 50 + 1.5
= 51.5m
So, the required height of the tree is 51.5m.
Example 5: A boy, 1.2m tall, is flying a kite. When the length of the string
of the kite is 180m, it makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal line. At what
height is the kite from the ground?
Solution:
Let CK be the height of the kite from the ground, AB be the height of the boy and AK be the length of the string.

Here, AB = 1.2m
AK = 180m
Angle of elevation, ∠DAK = 30°
In rectangle ABCD,
AB = DC = 1.2m.
In right angled triangle ADK,
sin30° = p/h =
KD/AK = KD/180
or, ½ = KD/180
or, 2KD = 180
or, KD = 180/2 = 90m
Now, CK = KD + DC
= 90 + 1.2
= 91.2m
So, the kite is at a height of 91.2m from the ground.
Example 6: A man is 1.6m tall and the length of his shadow in the sun is 1.6√3
m. Find the altitude of the sun.
Solution:
Let AB be the height of the man and BC be the length of his shadow. Let θ be the altitude of the sun.

Here,
AB = 1.6 m
BC = 1.6√3 m
In right angled triangle ABC,
tanθ = p/b =
AB/BC
or, tanθ = 1.6/1.6√3
or, tanθ = 1/√3 =
tan30°
∴ θ = 30°
So, the required altitude of the sun is 30°.
Example 7: A man √3 m tall is 72 m away from a tower 25√3 m high. Find the
angle of elevation of the top of the tower from his eyes.
Solution:
Let AB be the height of the man, CD be the height of the tower and BD be the distance between the man and the tower.

Here,
BD = AE = 72 m
AB = √3 m
CD = 25√3 m
CE = CD – ED =
25√3 – AB
= 25√3 – √3
= 24√3 m.
Now, in right angled triangle AEC,
tanA = p/b =
CE/AE
or, tanA = 24√3/72 =
√3/3
or, tanA = 1/√3
or, tanA = tan30°
∴ A = 30°
So, the required angle of elevation is 30°.
Example 8: The top of a tree which is broken by the wind makes an angle of 60°
with the ground at a distance of 3√3 m from the foot of the tree. Find the height
of the tree before it was broken.
Solution:
Let AC be the height of the tree before it was broken, BD be the broken part of the tree and CD be the distance between the foot of the tree and the point on the ground at which the top of the tree touched.

Here,
CD = 3√3 m
Angle of elevation, ∠CDB = 60°
In right angled triangle BCD,
tan60° = p/b =
BC/CD = BC/3√3
or, √3 = BC/3√3
or, BC = 9 m
Also, cos60° = b/h = CD/BD
or, ½ = 3√3/BD
or, BD = 6√3 = 6 ×
1.732 = 10.39 m.
∴ Height of the tree before broken = AC
=
AB + BC
=
BD + 9m
=
10.39m + 9m
=
19.39m
So, the required height of the tree was 19.39 m.
Example 9: Two vertical poles are fixed 60 m apart. The angle of depression of
the top of the first pole from the top of the second pole which is 150 m high
is 30°. Find the height of the first pole.
Solution:
Let AB be the height of the first (shorter) pole, CD be the height of the second (taller) pole and BD be the distance between them.

Here,
BD = AE = 60 m
CD = 150 m
The angle of depression = angle of elevation = ∠CAE = 30°.
In right angled triangle CEA,
tan30° = p/b =
CE/AE = CE/60
or, 1/√3 = CE/60
or, CE = 60/√3
or, CE = 34.64 m
Again, in rectangle ABDE,
AB = DE = CD
– CE
= 150 – 34.64
=
115.36 m
So, the required height of the first pole is 115.36 m.
Example 10: Two men are on the opposite side of a tower 30 m high. They
observed the angle of elevation of the top of the tower and found it to be 30° and
60° respectively. Find the distance between them.
Solution:
Let AB be the height of the tower and CD be the distance between the two men.

Here, AB = 30m.
Angle of elevations, ∠BCA =30° and ∠BDA = 60°.
In right angled triangle ABC,
tan30° = p/b =
AB/BC
or, 1/√3 = 30/BC
or, BC = 30√3 = 30 ×
1.732 = 52.05 m
Again, in right angled triangle ABD,
tan60° = p/b =
AB/BD
or, √3 = 30/BD
or, BD = 30/√3 =
30/1.732 = 17.32m
Now, CD = BC + BD
= 52.05 + 17.32
= 69.37 m
So, the required distance between the men is 69.37m.
If you have any question or problems regarding the Height and
Distance, you can ask here, in the comment
section below.
Was this article helpful? LIKE and SHARE with your friends…



Can you please solve the question which is given below:-
ReplyDeleteTwo boys of Same height of 1.2 m are flying kites at the same place. One of them takes away 25 m long thread which makes an angle of 45⁰ with the horizontal line whereas next takes away 35 m long thread which makes an angle of 60⁰ with the same horizontal line. If both kites are in same vertical line. Find how high the kite of the second boy is to the first boy.
Ans :- 7.07 m
Here is the solution to your problems,
Delete[image src="https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/a/AVvXsEgDTApwQ7B2T3aXNAOByd8i2cTSDo_WEIXhRvbEK0RjvxYZGfSfGQpmnlxrjbpqqhl0bccA-x5Xbq7tMxa3zAZCBJUKtUkFtl9iocgJ7WBLM8OfZ5-INTCmKLvbbWkqsWQVfIrl50AveSAEgEPlGKNogFJzLMbP-GysJirkevYfKh7Dpgli_VdAOTS3Eg=s16000"/]
Hlo
ReplyDeletethe angle of depression and elevation of the top of tower 50m high from top and bottom of second tower 45 degree and 30 degree respectively.Find the height of second tower
ReplyDeleteHere is the solution to your problem,
Delete[image src="https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/a/AVvXsEgaFlQiWSc8Z5475g3JoBMjKdj1SQnLB3PhWjaqC2L1SsSsY3U4pQ_yknR8R9SltheQlKXD-GBtCrgwoSgGQgTMJfQl65hyjjEUNc6qHmguvUxDPQ2ECqPStdnP49YPGv_KZbZDHpo86T24S_sJVcfXNLQgfHlRtQ3Jmi-fEPVrpnQNGoVyzF1JR6m6eg=s16000"/]
A tree of 14m height is broken by the wind so that its top touches the ground and makes an angle of 60° with the ground. Find the height of the broken part of the tree.
ReplyDeleteHere is the solution to your problem,
Delete[image src="https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh0Kiz4bPuiO11IYQWqJd9pmjmEFwijIs1VbOa3stbpOaVg4z-_B3PiwftmL5HqbDancNZWP6HDdW12vx640c8vbAXRT8oI1QiV8uWOg3cU7V5tq_mpTipsHSCaXxEtTDwSSKsMOrtbDLBTZEuYgDwnEVvMKiFuXkGTUiser3mASeift32FUBJQfe3e3Q/s16000/comment3.png"/]
From the top of a building 20 m high, a 1.7 m tall man observes the elevation of the top of a tower and finds it 45°. If the distance between the building and the tower is 50 m, find the height of the tower.
ReplyDelete