
Pythagoras (who died about 500 BC) was a Greek philosopher. He was a geometer
and a great mystic, who with his followers, seems to have been the first to
take mathematics seriously as a study in its own right as opposed to being a
collection of formulae for practical calculation. The Pythagoreans are credited
with the discovery of the well-known “Pythagoras
Theorem” on right-angled triangles.
Right-angled Triangle and Its Components
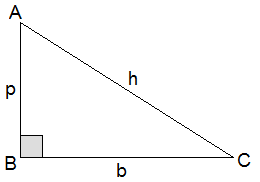
A triangle having one angle right angle i.e. 90° is called a right-angled triangle. In a
right-angled triangle, the opposite side of the right angle is called the
hypotenuse (h) and the other two sides are called the perpendicular (p) and the
base (b). In the figure alongside, ∠B = 90°, AC is the
hypotenuse (h), AB is the perpendicular (p) and BC is the base (b). In a right-angled triangle, the hypotenuse is the longest side.
********************
10 Math Problems officially announces the release of Quick Math Solver and 10 Math Problems, Apps on Google Play Store for students around the world.
********************
********************
Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagorean Theorem probably is the best-known theorem in geometry, which gives the
relationship between the lengths of sides of a right-angled triangle.
Pythagorean Theorem states that: “In a
right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the
squares of perpendicular and base.”
i.e. h2 = p2
+ b2
This Pythagorean relation is widely used in mathematics,
physics, astrology, geology, engineering, etc.
Derived Relations
From the above Pythagorean relation, we can have the following
derived relations:

Pythagorean Triple
A set of three positive integers a, b and c such that a2
+ b2 = c2 (Pythagorean relation) are called Pythagorean Triple. If {a, b, c} is a
Pythagorean Triple, then so is {ka, kb, kc} for any positive integer k.
Pythagorean triples that have the highest common factor 1 include the
following: {3, 4, 5}, {5, 12, 13}, {8, 15, 17}, {7, 24, 25} and {20, 21, 29}
etc.
Application of Pythagorean Theorem
Worked Out Examples
Example 1: The area of square A is 21cm2 and the area of square C is 33cm2, find the area of square B.

Solution: Here,
Area of square A = 21cm2
Area of square C = 33cm2
Area of square B =?
Using Pythagoras theorem,
Area of square C = Area of square A + Area of square B
i.e. 33cm2 =
21cm2 + Area of square B
or, Area of square B =
33cm2 – 21cm2
or, Area of square B =
12cm2
∴ The area of square B is 12cm2.
Example 2: Calculate the value of ‘x’ in the adjoining right-angled triangle.

Solution: Here,
From the adjoining figure,
Perpendicular (p) = 3cm
Base (b) = 4cm
Hypotenuse (h) = x = ?
We know that,

∴ x = 5cm
Example 3: The upper part of a tree is broken by the wind and the rest is 20m
long. If the top of the tree lies 21m from the foot of the tree then find the
length of the broken part of the tree.
Solution: Figure:

Height at which the tree has been broken (p) = 20m
The distance between the foot of the tree and the point where the broken part touches the ground (b) = 21m
Length of the broken part of the tree (h) =?
According to the Pythagoras theorem,
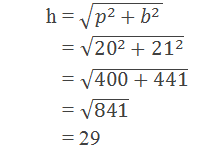
∴ The length of the broken part of the tree is 29m.



0 comments: